Scalp psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the scalp, causing red, itchy plaques covered with silvery scales. Understanding its symptoms, underlying causes, and available treatments is crucial for effectively managing this condition and improving quality of life.
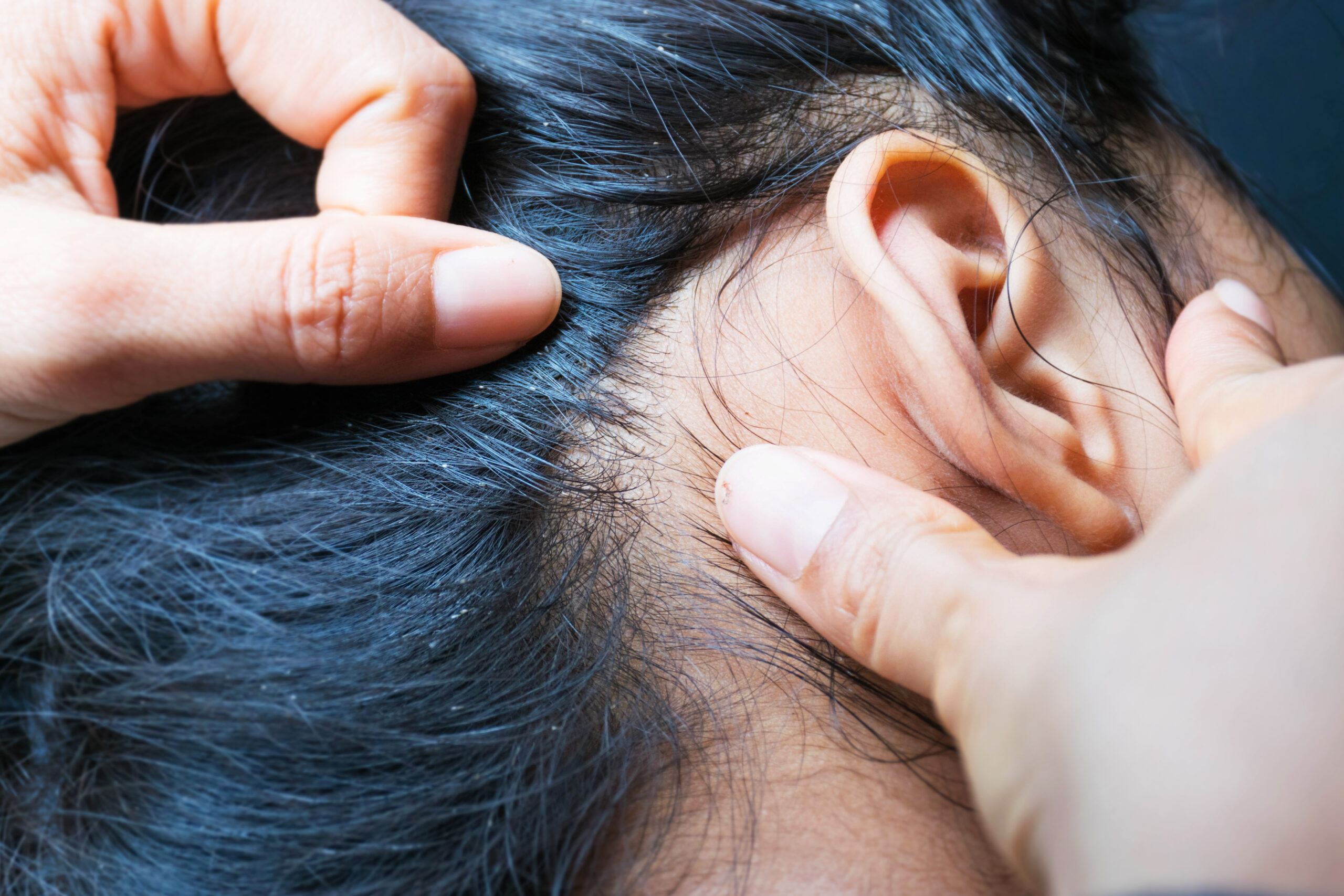
Symptoms of Scalp Psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis presents with several distinct symptoms:
- Red, Scaly Patches: These patches often appear raised and can extend beyond the scalp onto the forehead, neck, and ears.
- Itching and Discomfort: Scalp psoriasis can be intensely itchy, leading to scratching that may worsen symptoms and cause hair loss.
- Silvery Scales: The scales, caused by excessive skin cell turnover, can flake off and resemble dandruff, but they are thicker and more adherent.
- Dryness and Cracking: The affected areas may become dry, leading to cracks and bleeding in severe cases.
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of scalp psoriasis is complex and involves genetic, immune, and environmental factors:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history plays a significant role, as psoriasis tends to run in families.
- Immune System Dysfunction: An overactive immune response triggers rapid skin cell turnover, leading to the characteristic scaling and inflammation.
- Environmental Triggers: Factors such as stress, infections, and certain medications can exacerbate or trigger flare-ups.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosing scalp psoriasis typically involves a physical examination by a dermatologist:
- Visual Inspection: The dermatologist examines the scalp and affected areas to identify characteristic symptoms like redness, scaling, and plaques.
- Differential Diagnosis: Conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, and fungal infections can mimic scalp psoriasis, requiring careful differentiation for accurate diagnosis.
Effective Treatments for Scalp Psoriasis
Managing scalp psoriasis involves a combination of medical treatments and self-care strategies:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams, shampoos containing salicylic acid, and vitamin D analogs can reduce inflammation and scale buildup.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can slow skin cell turnover and reduce inflammation, often administered under medical supervision.
- Systemic Medications: In severe cases, oral or injectable medications that target the immune system, such as biologics and retinoids, may be prescribed.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Managing stress, avoiding triggers like harsh hair treatments or excessive scratching, and maintaining a healthy scalp hygiene routine can complement medical treatments.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Some individuals with scalp psoriasis find relief through alternative therapies:
- Natural Remedies: Aloe vera, coconut oil, and tea tree oil may soothe scalp irritation and reduce scaling, although their effectiveness varies.
- Dietary Adjustments: Some evidence suggests that anti-inflammatory diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants may help reduce inflammation associated with psoriasis.
Living with Scalp Psoriasis
Living with scalp psoriasis involves ongoing management and support:
- Educational Resources: Accessing reliable information and support groups can help individuals better understand their condition and manage its impact on daily life.
- Regular Follow-ups: Routine visits to a dermatologist ensure treatment effectiveness, monitor for potential side effects of medications, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Conclusion
Scalp psoriasis is a challenging yet manageable condition that requires a tailored treatment approach based on individual symptoms and severity. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and available treatments, individuals can take proactive steps towards effectively managing scalp psoriasis and improving their overall well-being.
References
- National Psoriasis Foundation. (n.d.). Scalp Psoriasis. Retrieved from https://www.psoriasis.org/scalp-psoriasis/
- American Academy of Dermatology. (n.d.). Scalp Psoriasis. Retrieved from https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/psoriasis/psoriasis-resource-center/scalp-psoriasis